Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
This article does not constitute as medical advice.
If you are experiencing symptoms, contact your doctor or make an appointment.
This article does not constitute as medical advice.
If you are experiencing symptoms, contact your doctor or make an appointment.
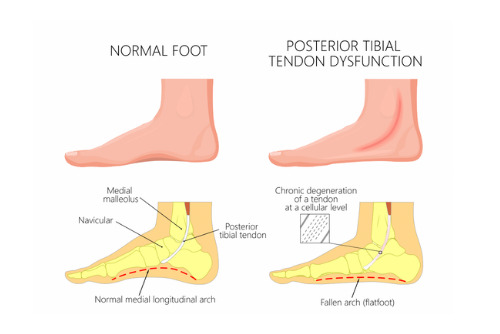
The posterior tibial tendon attaches the calf muscles to the bones in the foot. Its function is to provide support for the arch and hold up the muscles in the foot. Inflammation or tearing of this tendon causes pain and poor foot support, known as posterior tibial tendonitis. Over time it can result in a flat foot or arthritis. This condition is one of the most common foot and ankle problems.
This condition commonly occurs when people overexert themselves or spend too much time on their feet. Here, the tendon becomes inflamed and irritated, leading to PTTD after a time.
PTTD is associated with pain in the foot, ankle, and calf. Discomfort worsens if left untreated. Therefore, be sure to seek treatment early when you first start to experience symptoms! Be on the lookout for:
Pain: Patients tend to experience pain in the lower leg and ankle, especially when moving uphill or going up the stairs. Pain will worsen with increased activity.
Redness and swelling: When the injury first occurs, redness and swelling may appear on the foot or ankle.
Flattened arches: In the later stages of this condition, the foot’s arch will flatten out. Consequently, having less support in the foot with flat arches can lead to more injuries down the road.
If caught early, those with PTTD can treat it at home with rest and proper support. However, many patients with this injury are athletes or other active people, so slowing down can be challenging! Without a suitable resting period, symptoms can worsen, and surgery may be required.
At-Home Treatment:
Medical Treatment: