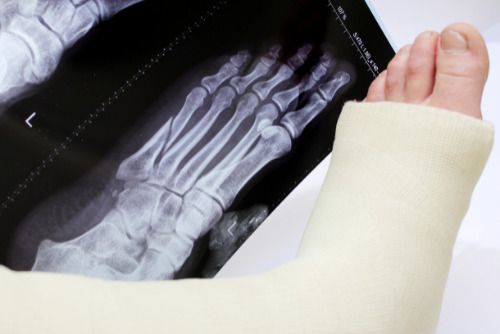
Stress Fractures
This article does not constitute as medical advice.
If you are experiencing symptoms, contact your doctor or make an appointment.
This article does not constitute as medical advice.
If you are experiencing symptoms, contact your doctor or make an appointment.
Stress fractures are tiny breaks in the bone caused by overuse, repeated pressure, or weakness from conditions like osteoporosis or aging. This condition is also common if shin splints are left untreated. To treat stress fractures, patients will need rest or immobilization and may take weeks to heal. Therefore, it is essential to understand and assess the cause of the stress fractures so that patients can address the issue to avoid further injury.
Repetitive pounding and wear and tear cause tiny breaks in the bones. Here are some specific factors that lead to the weakening of the feet and legs:
Pain that increasingly worsens is a sign of a fracture. If you are experiencing these common symptoms, contact your podiatrist.
Patients with this condition may be out of commission for their sport or activity for weeks at a time for proper healing. To keep healthy, here are ways to prevent and treat stress fractures.
Prevention
Treatment: